TanazaOS and OpenWRT – Differences and similarities
Press play to listen to the article.
A guide to OpenWRT and TanazaOS. A comparison of the features of these two operating systems for embedded devices.
What is OpenWRT?
OpenWRT is a well-known open-source (GPL license) Linux distribution for embedded systems like routers, wireless access points, and CPEs.
It has been widely used for multiple applications in wireless networking, thanks to the wide range of extensions available.
What is TanazaOS?
TanazaOS is a proprietary operating system by Tanaza.
First released in 2019, it is a Linux-based operating system for Wi-Fi access points. At the contrary of firmware versions 1.x and 2.x released by Tanaza until 2019, it is not based on OpenWRT.
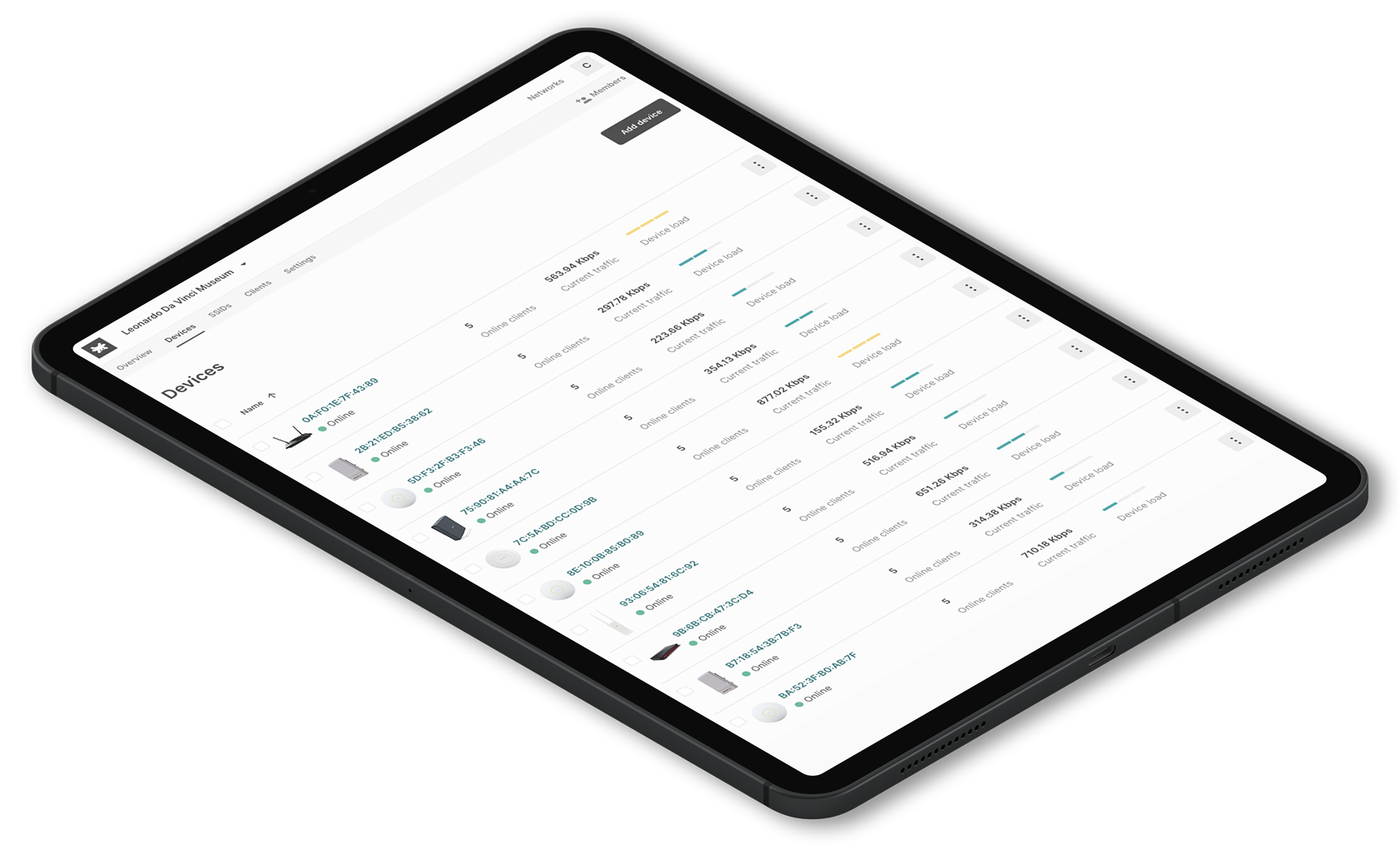
The LuCi Web Interface and Tanaza’s cloud-based interface
Both OpenWRT devices and TanazaOS devices are managed through a web interface. However, LuCi (the OpenWRT web interface) is not as intuitive as Tanaza’s.
Open-WRT allows managing single networking devices through commands. Instead, Tanaza includes a cloud-based intuitive interface to manage multiple Wi-Fi networks in a centralized way.
Supported wireless access points
The lists of compatible hardware for OpenWRT and TanazaOS differ significantly: OpenWRT supports a broader variety of devices, including CPEs and routers.
Similarly, they both make releases for old devices, therefore prolonging the life of the hardware with the software.
TanazaOS and OpenWRT features
Both operating systems allow adding new functionalities to the access points.
While in Tanaza these features are available within the platform without any need for coding, Open-WRT requires coding extension packages. Examples of application extensions include a captive portal, bandwidth control, VLANs, reducing latency/lag, securing internet access.
Tanaza also allows integrating the platform with a large variety of external systems. Both TanazaOS and Open-WRT free their users from the application selection provided by the hardware manufacturer.
TanazaOS and OpenWRT security and quality assurance
Both TanazaOS and Open-WRT are resistant to common vulnerabilities, are stable, and operate reliably for long periods. Thanks to the frequent software updates also for older devices, there are no hidden backdoors left by hardware vendors.
Tanaza is a for-profit company partnering with leading vendors. It is pro-actively acting to keep its firmware 100% bug-free and safe. Tanaza’s Quality Assurance team performs hundreds of tests to ensure the full functionality of the firmware and the platform. Tanaza is a production-ready, proven enterprise-grade product with over 12 releases/year.
Instead, the Open WRT project relies on its releases (around one/year) on the work of the OpenWRT community. Consequently, it does not go through a precise quality assurance process. Releases sometimes lead to breakages in some system’s elements or previously available functionalities.
Operational efficiency with Tanaza and OpenWRT
The fundamental difference between Open-WRT and Tanaza is that the last is much easier to use and intuitive.
OpenWRT is a valuable open-source project. However, it does not allow cloud managing and monitoring Wi-Fi networks in a fast and efficient way.
Book your Guided Demo today!
This guided demo will help you understand how to use the different features the Tanaza platform offers. Speak directly with one of our experts.
✔︎ No credit card required