NARA & Tanaza’s AI journey

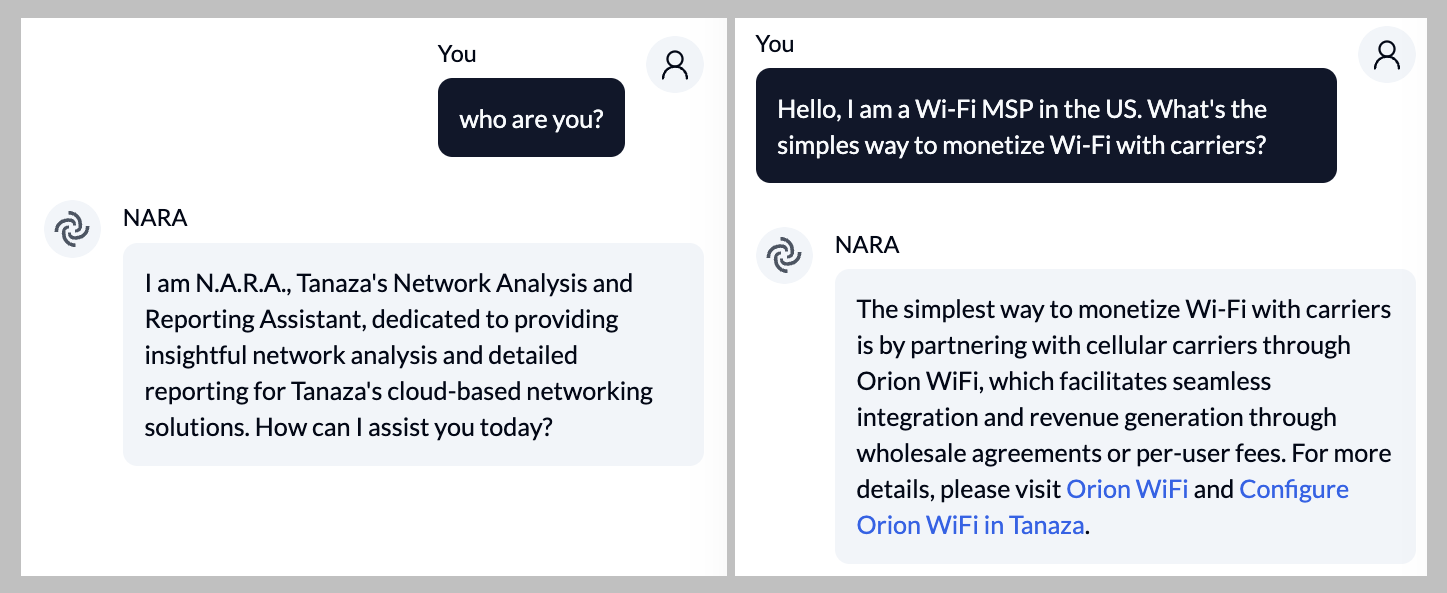
NARA: Tanaza’s AI-powered assistant
Since the release of GPT-3.5 at the end of 2022, it became clear that AI was finally getting ready to significantly impact all industries. As tech enthusiasts who have dedicated the past decade to cloud computing and networking, we were eager to explore the potential of AI in our field.
Our journey began with extensive research, testing various AI options, and refining our concepts. By December 2023, we launched the Tanaza GPT agent integrated with ChatGPT. Today, I am thrilled to introduce NARA, our AI assistant.
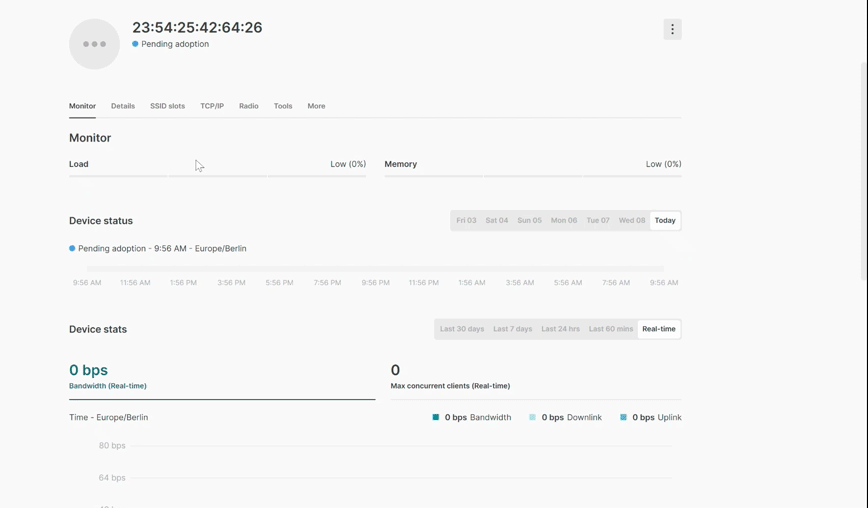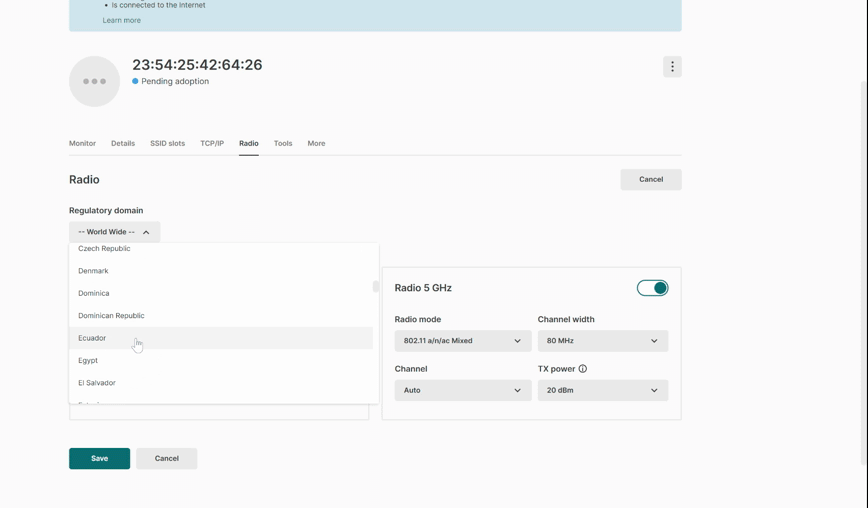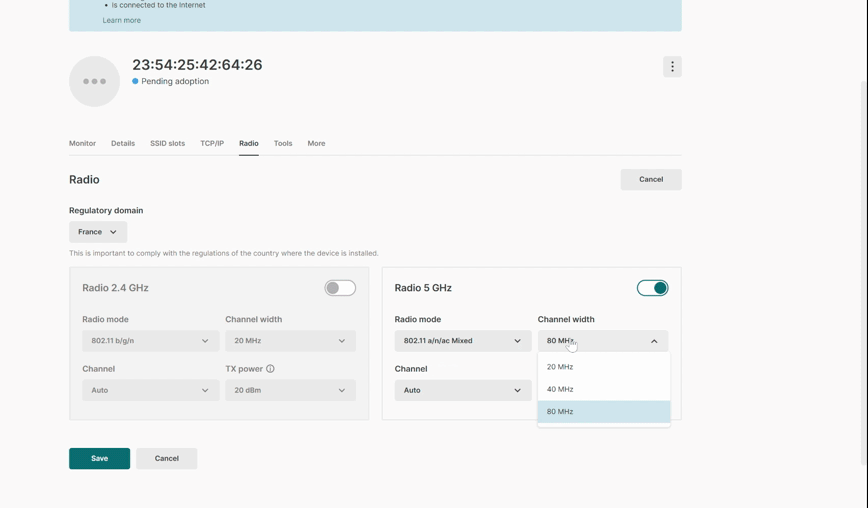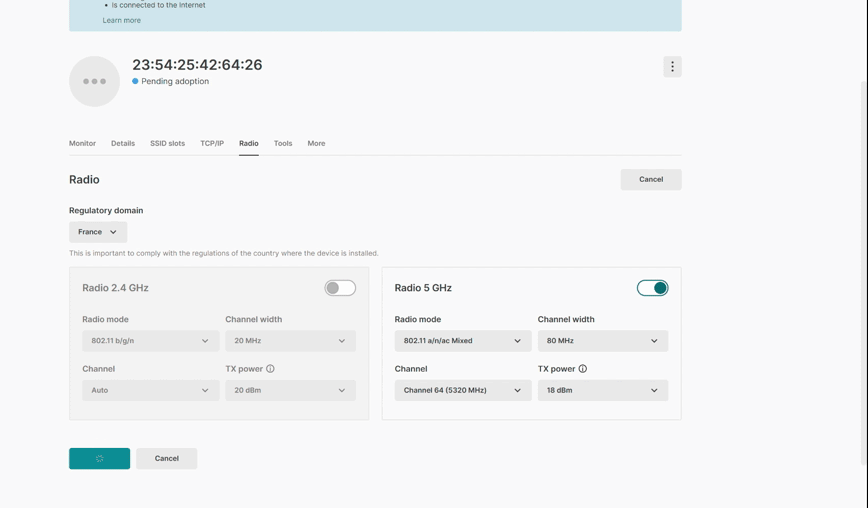
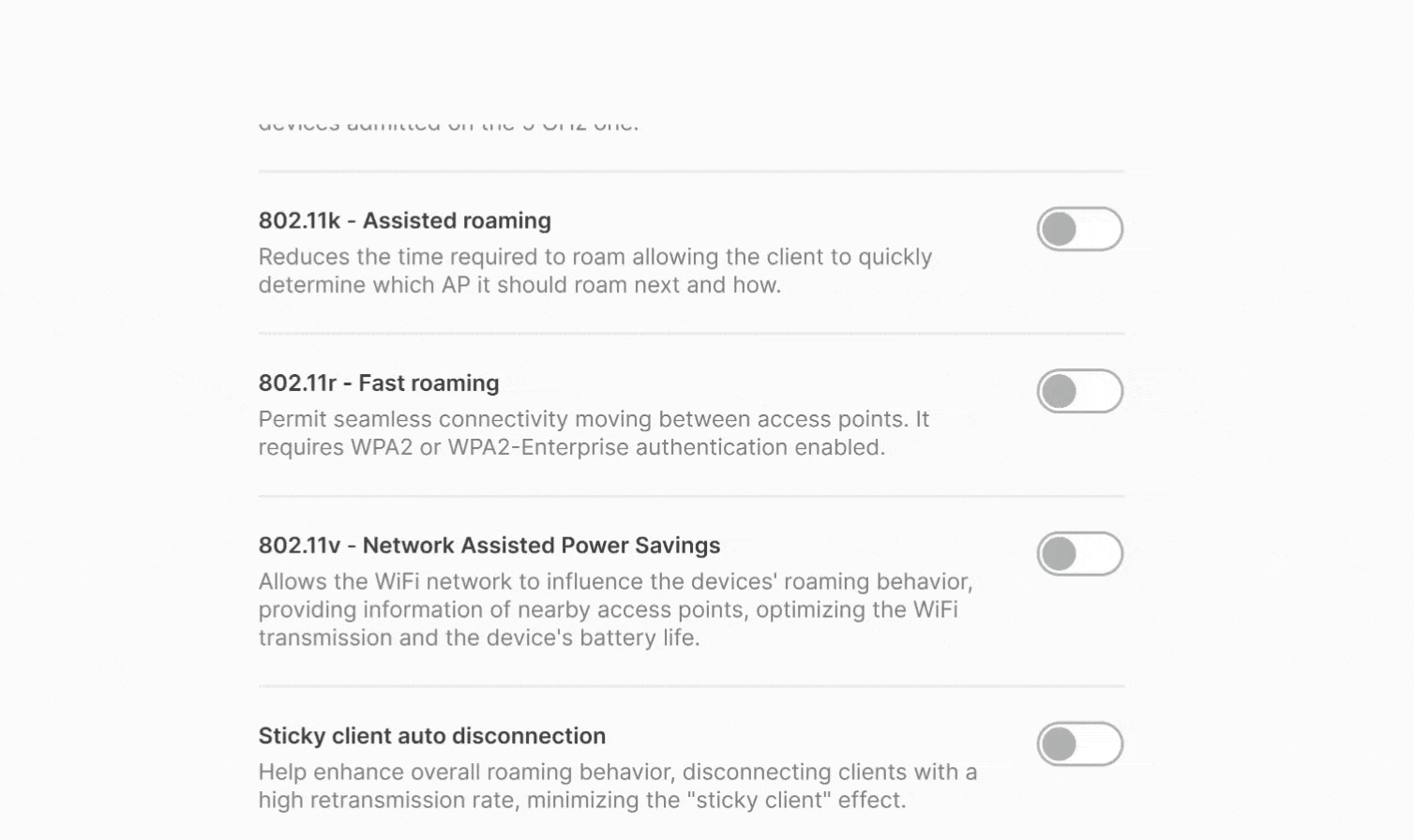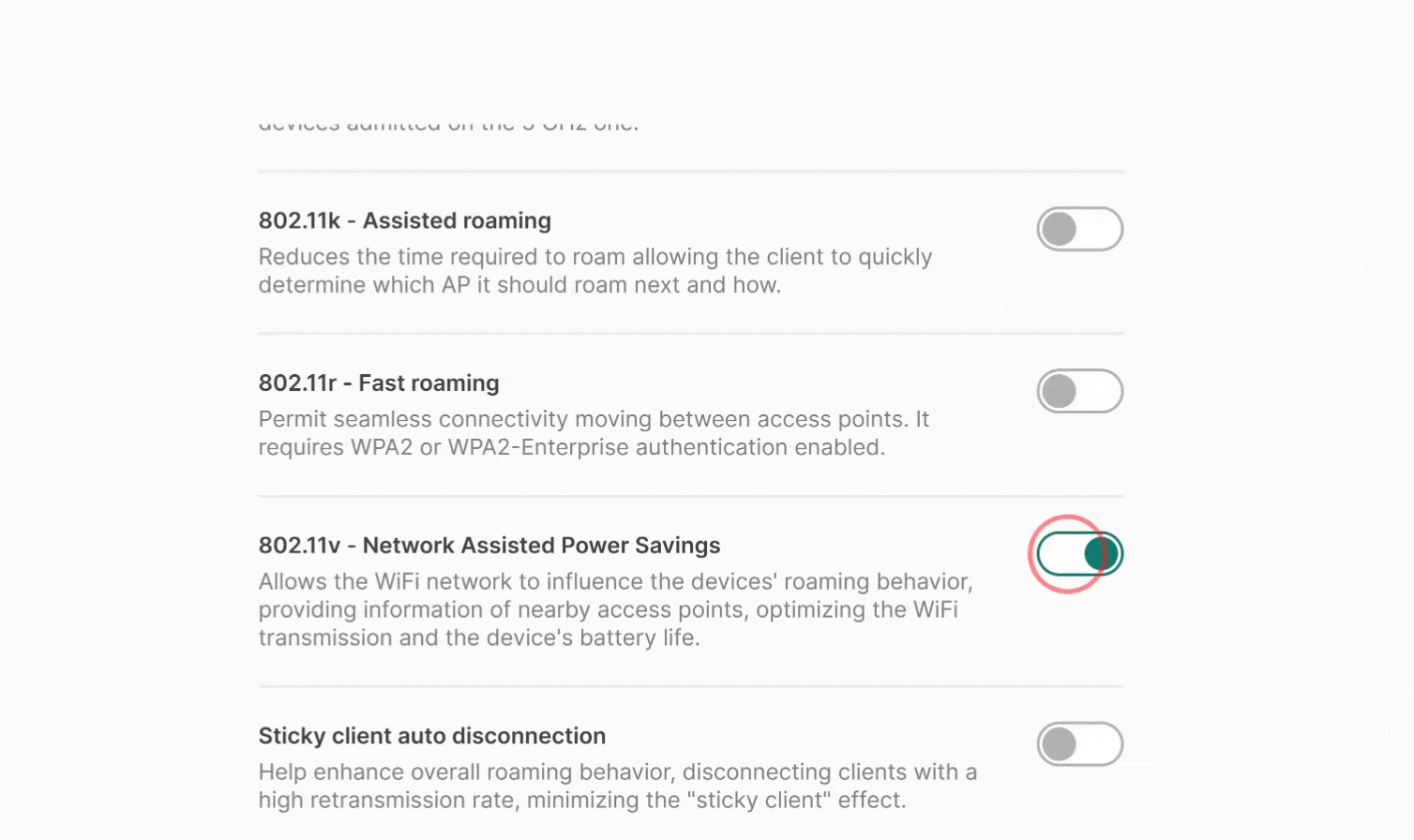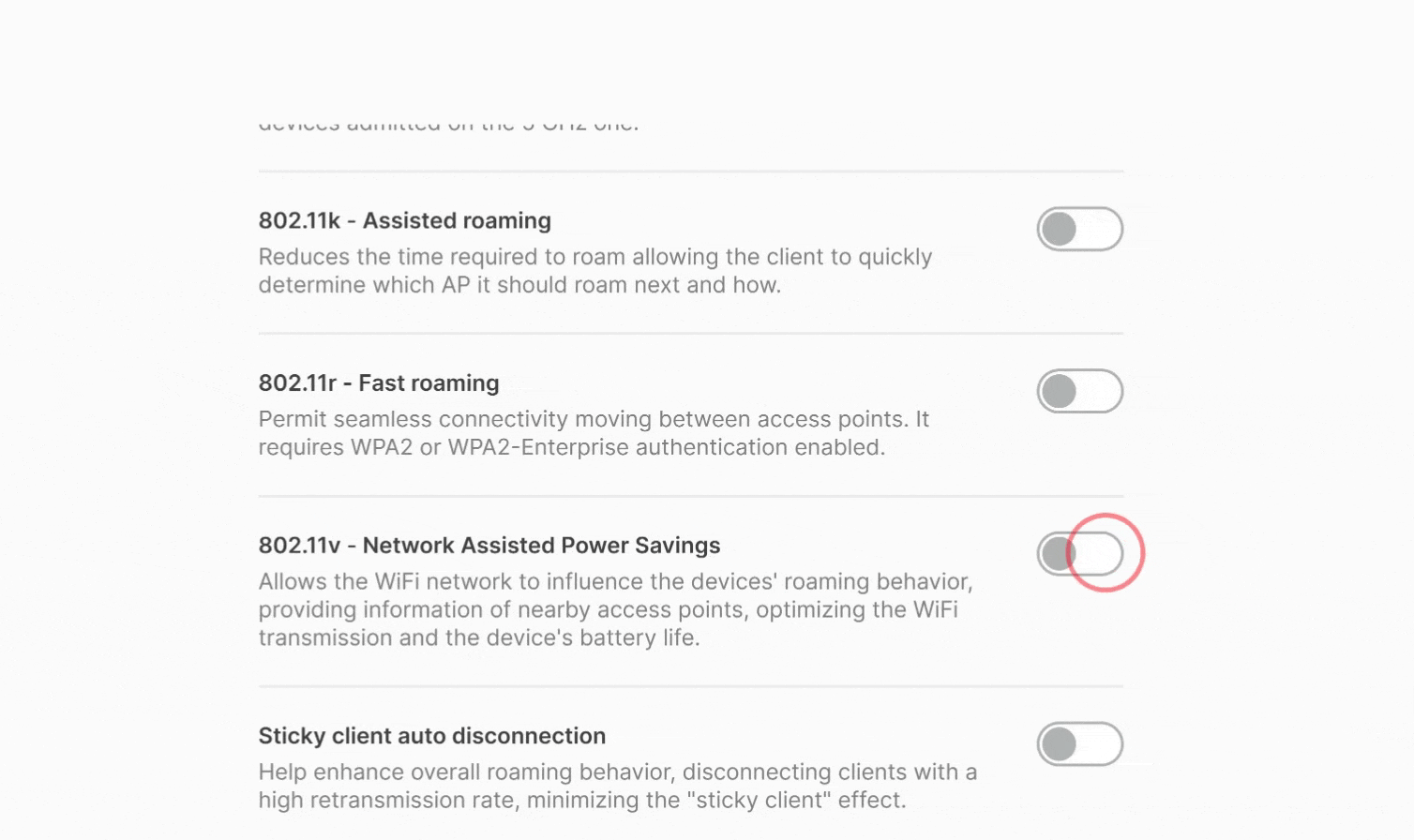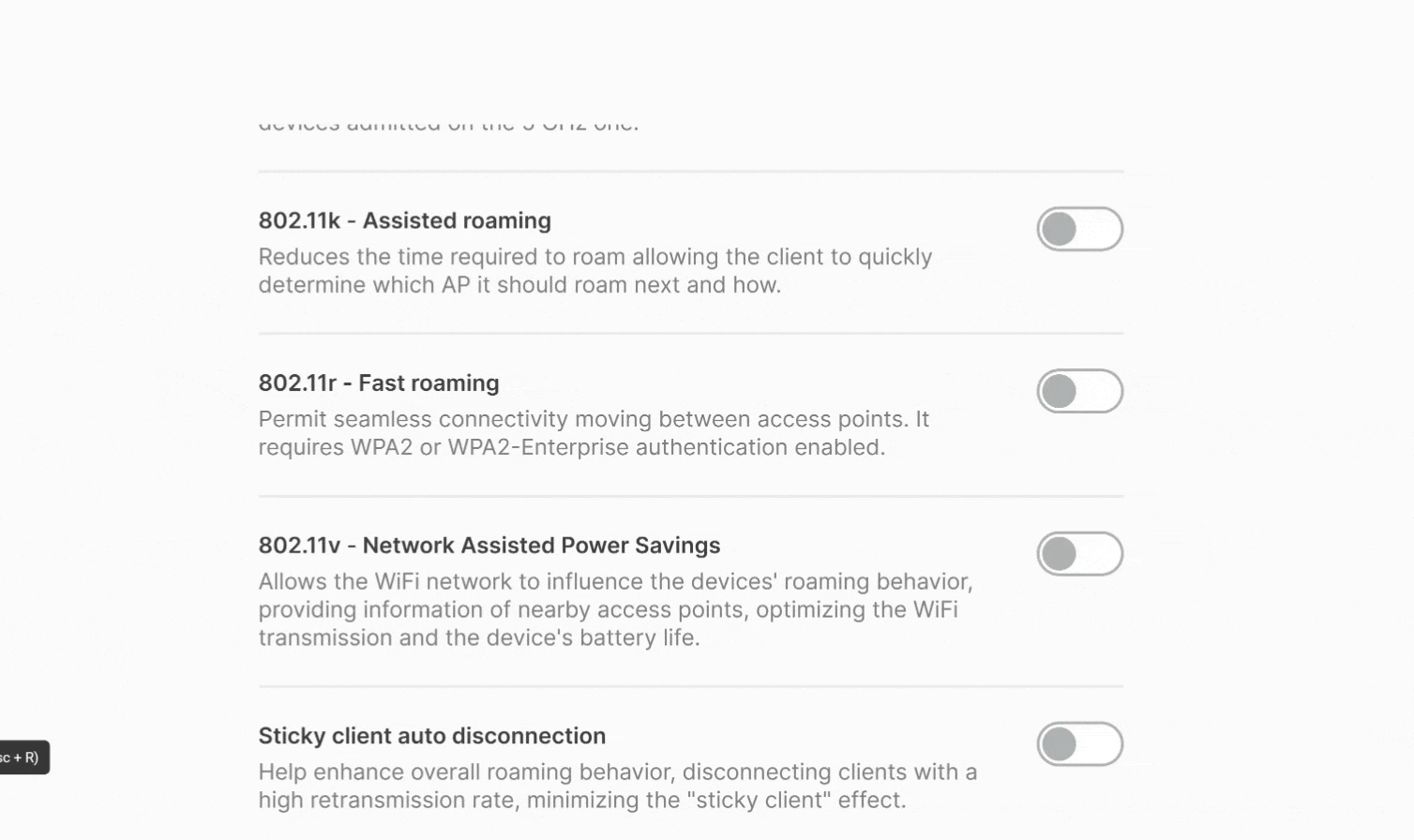
NARA is designed to assist Tanaza users at every stage of their journey: from initial discovery and evaluation to adoption and large-scale operations. It can answer specific questions in real-time, help get started with Tanaza or provide guidance to troubleshoot networks. Furthermore, it can recommend the best Apps from our marketplace based on users’ needs. These are capabilities that are already available and we encourage you to play with it on support.tanaza.com.
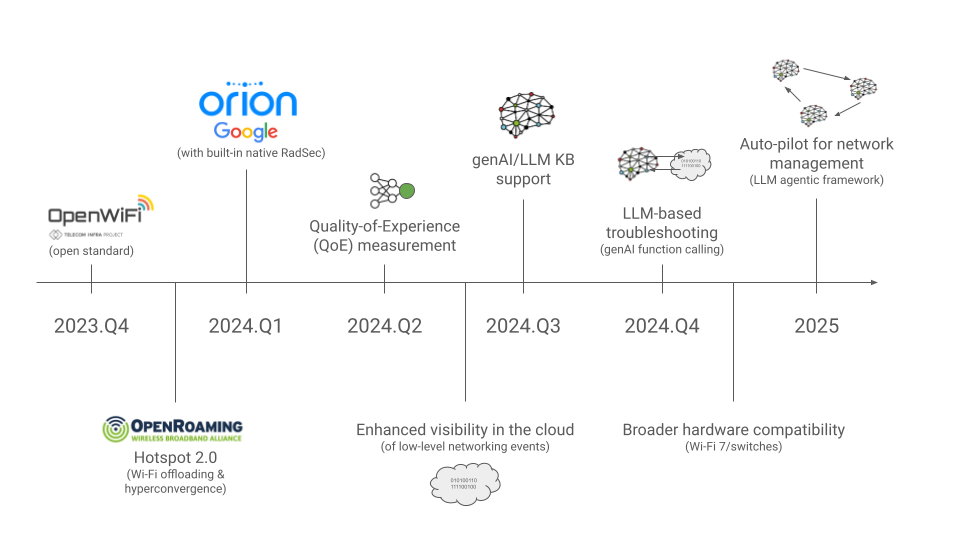
Tanaza’s AI journey and lessons learned so far
Our ultimate vision is for NARA to fully automate Wi-Fi and enterprise networks, making them entirely AI-driven. We believe this is achievable, and this is fully reflected in our high-level roadmap.
The path to this point has been challenging. Despite the amusement generated by ChatGPT (when it gets it right), developing a controlled AI that performs precisely as needed and avoids hallucinations is akin to “keeping a wizard inside a cage“. We evaluated various chatbot solutions and found that existing tools required significant tuning and curated knowledge to function correctly. We needed an AI that adhered to our principles and met our specific needs.
Additionally, we’ll need to integrate authentication systems, connect to our knowledge base and production systems with different access levels, and ensure consistency with our privacy policy. We aimed to learn from thousands of cases and conversations in our CRM while protecting private information. These requirements led us to build a system that is both open and controllable. In a rapidly evolving context, we chose to create a framework that leverages the latest LLM models while maintaining full control of all aspects.
Here are the key guiding principles we adopted:
- MVP Approach: Start with a minimum viable product and expand its scope over time.
- LLM Agnostic: Our framework can leverage the most efficient models, whether from LLAMA, OpenAI, Claude, or others.
- Curated Knowledge: Knowledge must be carefully curated, whether created by humans or synthesized from multiple sources.
- Unified Agent: Instead of multiple agents for different purposes, we opted for a single source of truth representing our company’s knowledge. This makes the problem harder to solve, but delivers an incredible experience to users.
- Regression Protection: Automatic testing is crucial, with a different LLM testing the output of each test case.
- Coachability: Any Tanaza senior employee should be able to train our AI, similar to how they mentor junior employees. Coaching NARA has been exhilarating (like giving input to Johnny 5).
- Extensibility: Starting with 0-shot learning, the AI will evolve to deeper connections with production systems, real-time diagnostics, and ultimately an always-on AI agent capable of auto-driving networks.
This journey is incredibly exciting. The potential applications of AI in networking are limitless, and we are proud to bring these capabilities to our users, adding the AI pillar to our core principles of cloud and hardware/software disaggregation.
A big thank you to all of our users and partners for joining us on this journey in building next-gen AI-powered infrastructure.