Network downtime – The real cost for MSPs, ISPs and SPs

Network downtime – The real cost for MSPs, ISPs and SPs
Network downtime is one of the most expensive issues for MSPs, ISPs and SPs network architectures. It’s unavoidable, systematic and often unpredictable.
The most relevant study conducted by Gartner has demonstrated that network downtime can cost on average up to $9,000 per minute.
Organization size is also a key factor. For Fortune 1,000 companies, network downtime could cost as much as $1 million per hour, according to an IDC survey. And while the typical mid-sized company spends $1 million per year on incidents, large enterprises can spend up to $60 million or more, according to a research report from IHS.
Considering the pure math without taking in consideration generic case studies, also Cloudscale has mathematically demonstrated through a computational algorithm the relationship “network downtime = money loss”.
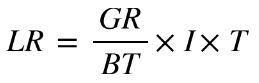
where
LR is the Lost Revenue
GR is the Gross yearly Revenue
BT is the total Business Time (in minutes)
I is the percentage of revenue impacted by the down time (an online retail business could see 100% impact whereas a sole proprietor insurance company could be 60%)
T is the downtime
Today the effects of a downtime have direct consequences on loss of company revenue.
Wherever is the cause of a network downtime, MSPs, ISPs and SPs have to consider implementing solutions to mitigate or prevent network downtime.
What are the causes of network downtime?
The IS-IS protocol (ISO/IEC 10589:2002 – included in the OSI model) classifies network downtime in six classes:
Level 0 – Network is down
Level 1 – Part of the network is down
Level 2 – Most of the network is down
Level 3 – All of the network is down except for a few isolated systems
Level 4 – Most of the network is down, but some systems are still functioning
Level 5 – All systems are functioning, but there are performance issues
These categories are used to help network administrators understand the extent of the network downtime and to identify the root cause of the problem. By understanding the level of downtime, administrators can prioritize their efforts to restore the network and minimize the impact on users.
What are the most common causes for network downtime at OSI Layers?
1) Faults, errors or discards in network devices (Layer 2)
2) Wrong device configuration changes (Layer 2)
3) Operational human errors and mismanagement of devices (Multiple Layers)
4) Link failure caused due to fiber cable cuts or network congestion (Layer 1-2)
5) Power outages (Layer 1)
6) Server hardware failure (Layer 4)
7) Denial of service (DoS) (Multiple Layers)
8) Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) (Multiple Layers)
8) Failed software and firmware upgrade or patches (Layer 7)
9) Incompatibility between firmware and hardware device (Layer 7)
10) Other external causes (Multiple Layers)
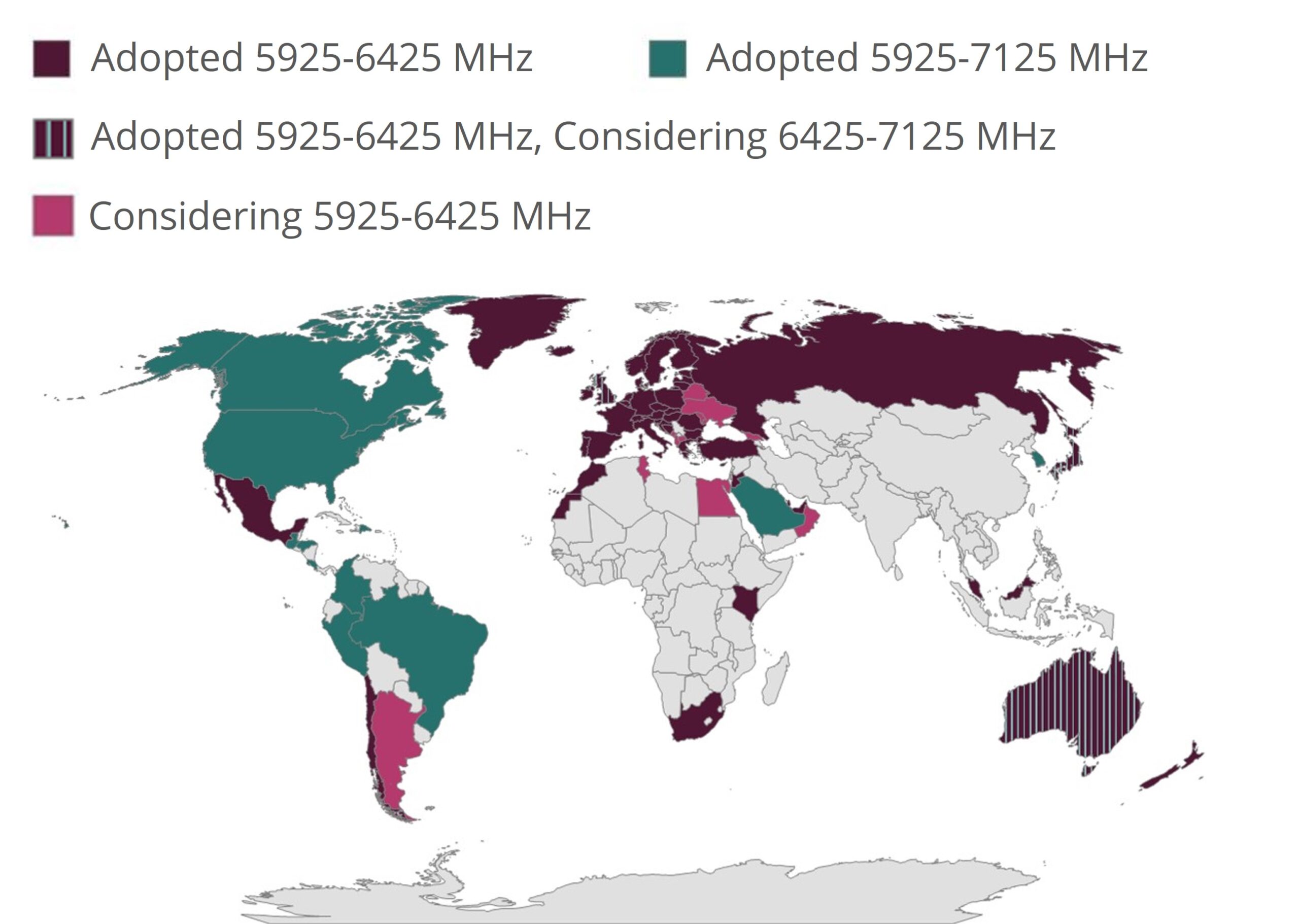
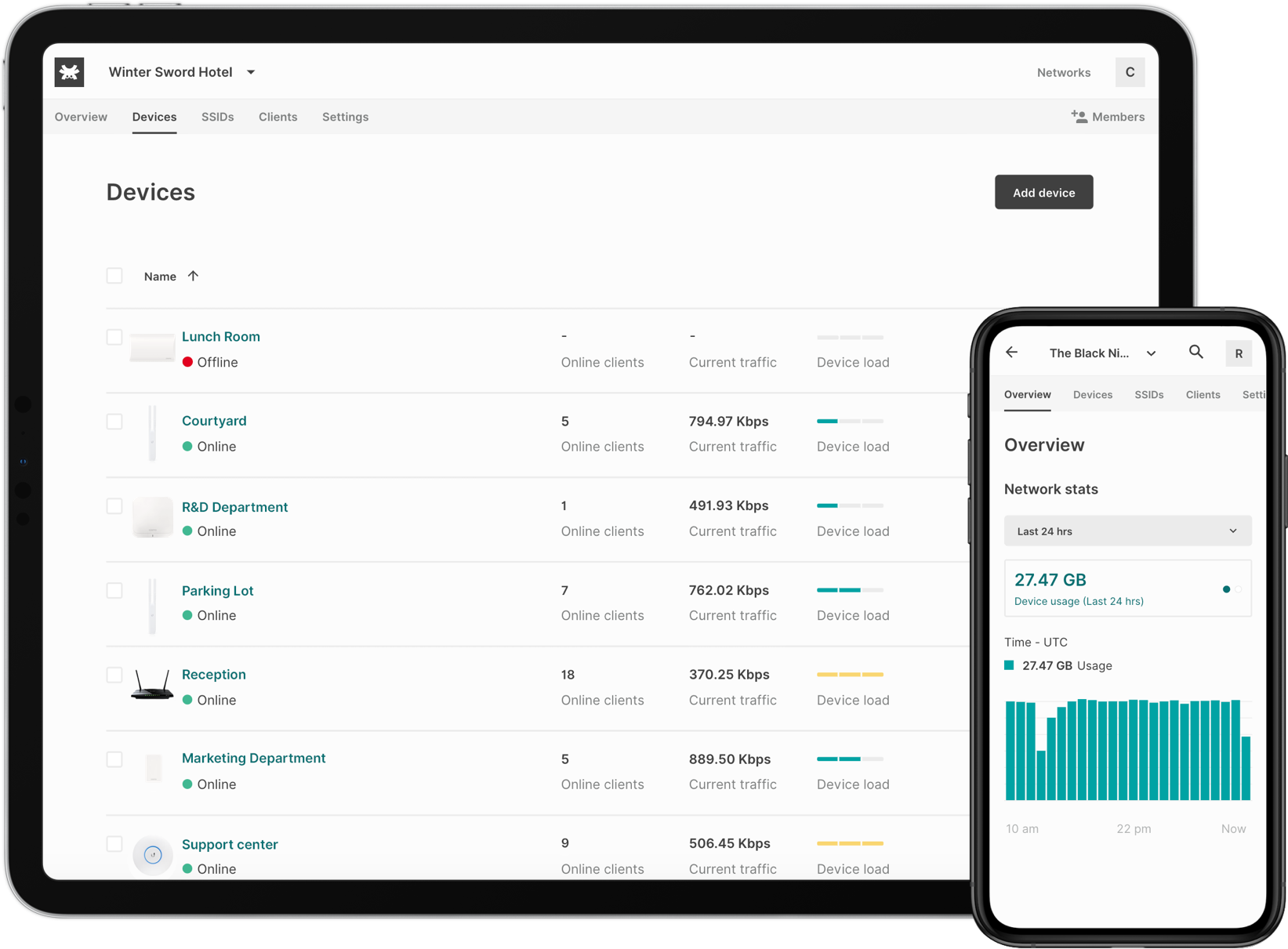
Fing App (now a Tanaza add-on) has precise and updated real-time and historical lists of network downtime, divided by countries, duration, recurrence, severity, impact. Network administrators can read details about each single network downtime or visualize them in bulk thanks to real-time interactive maps:
The importance of an outage detector system integrated in Tanaza WiFi cloud management
An outage detector system is a network management application that allows the monitoring of network infrastructure’s faults and errors, proposing solutions and tips to fix them and checking the ISP status.
Outage detector systems are fundamental for MSPs, ISPs, and SPs that want to reduce and prevent network issues and avoid the aforementioned costs caused by outages.
The activation of the Fing App in the Tanaza cloud platform allows to identify what network endpoint is hurt by the outage.
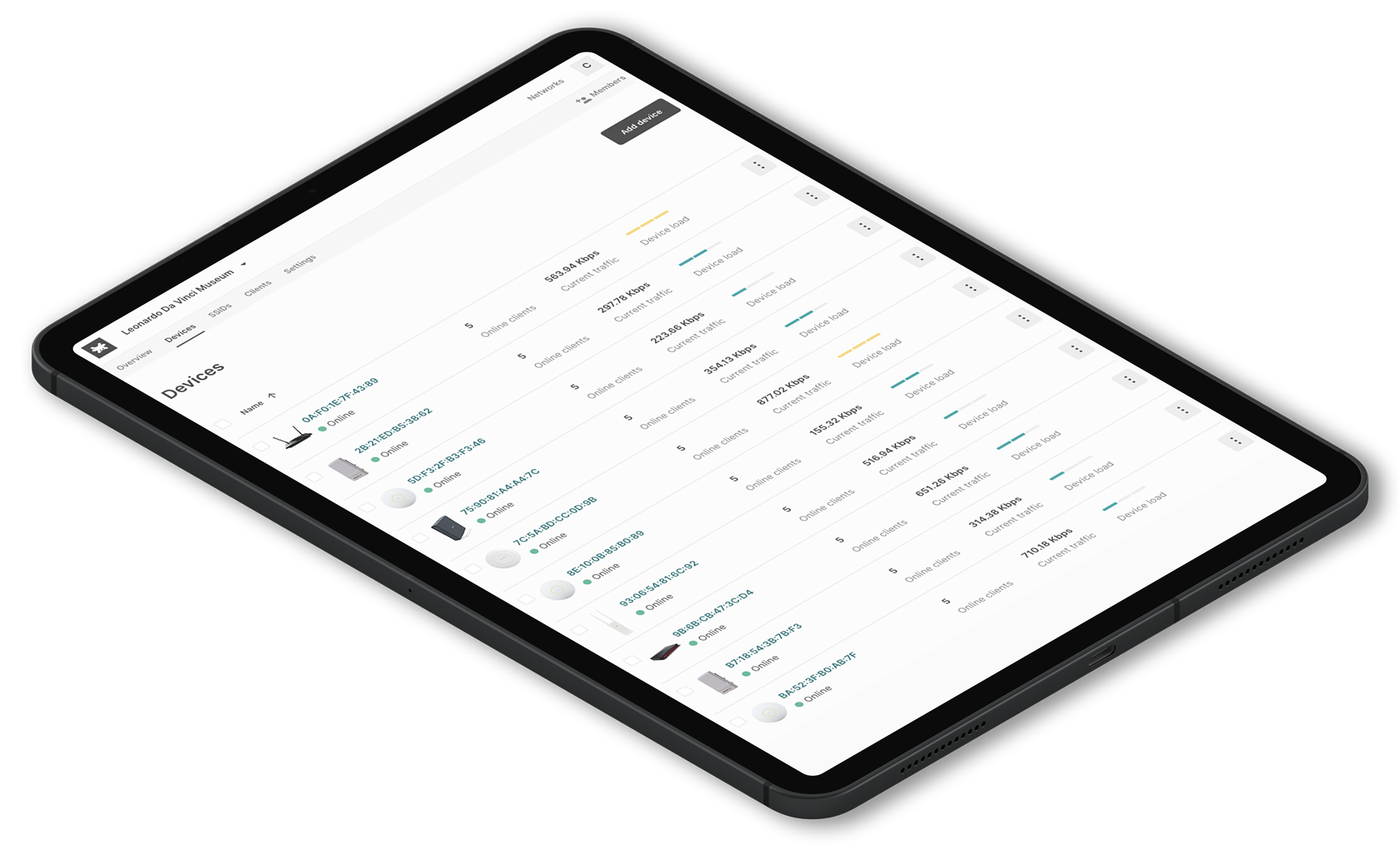
Network administrators can visually and fastly identify what types of clients (smartphone, laptop, printer, etc) are connected to the networks thanks to an intuitive list of minimal icons.
Depending on the chosen plan for the add-on, each client will show relevant network information including the status and the classification of connection, type and brand of WiFi client, bandwidth values (download and upload mbps) and OS information (name, version, build).
Fing and Tanaza have combined their core technologies to create the advanced outage WiFi notification system. Thanks to Tanaza + Fing add-on, network administrators can understand if the APs are offline for internet outages around the world, improving their efficiency to inform their customers about recovery times and responsibilities. The add-on is compatible with the main ISPs of each country and allows network managers to compare them by rating and reviews in order to identify in real-time the best solution for internet connection.
Fing App is able to register real-time ISP connection status data, including information about the severity of outage (on a scale of 5 values: minor, moderate, considerable, major, critical), outage duration and recurrence, and geographical impacted areas.
For this reason, Tanaza and Fing add-on is based on an AI-algorithm that operates in a fully automatic way, with no need for manual reporting.
Try the Tanaza + Fing add-on
Test the accurate identification of client devices connected to your multi-vendor networks.
✔︎ No credit card required ✔︎ Easy and fast integration
✔︎ Free up to 3 APs